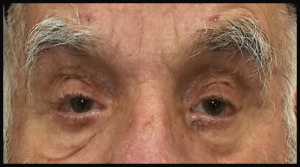
- Treatment for OPMD focuses on helping the swallowing problems, eyelid drooping, or limb weakness.
- An instructive training by speech-therapists will preserve and improve the strength of muscles of speech and swallowing.
- Occupational therapy will help you with adaptive methods for daily tasks.
- Modification of the diet and the texture of foods will make them easier to swallow.
- In some cases surgical procedures may be necessary to maintain adequate nutrition or to correct eyelid drooping or to suppress pooling of thick saliva.
- An accelerated development of genetic therapy that may correct the hereditary defect by injecting a drug into the damaged muscle is currently underway.
- Drooping eyelids (Ptosis)
- Swallowing problems (Dysphagia)
- Muscle weakness
Conservative non-surgical therapy
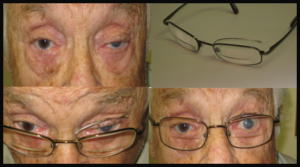
A device named EYELID CRUTCHES can be ordered from selected optometrists.
The photos below demonstrate a correction of drooping eyelid on the left by theEYELID CRUTCH adjusted in the frame of the glasses.
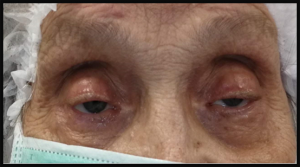
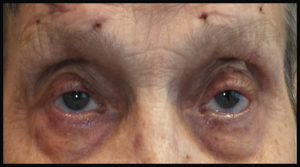
Surgical correction of the eyelid drooping
If the forehead muscles are not weakened by the disease, a surgical tie between the upper eyelid and the forehead FRONTALIS muscle (called FRONTALIS SLING) enables patients to lift the eyelid by lifting the forehead muscle – consequently, the visual filed can be restored.
In the photo below – a patient before and 1 month after surgery to correct drooping eyelids – with satisfactory recovery.
The goals of management of OPMD-related dysphagia are to improve food transfer and prevent aspiration. In early stages of OPMD-related dysphagia, swallow training and dietary modification can improve swallowing and reduce a risk for aspiration. Relatively simple techniques that has been used in relieving the dysphagia in OPMD can be viewed here.
-
Oral motor exercises can strengthen the muscles that control drooling and assist in food and drink propulsion. The exercises listed here require no more than 10 minutes to complete and practicing these should start as soon as the diagnosis of OPMD has been made.
-
The supraglottic swallow technique improves airway protection during swallowing. An instructive video can be viewed here.
-
Use of Mendelsohn’s maneuver can assist in food propagation as well as protection of the airway from potential aspiration. An instructive video can be viewed here.
-
Meals taken during times of maximal attentiveness are more easily swallowed.
-
Dietary modification may also improve swallowing and help avoid aspiration. Thickening of food texture by cooking techniques or by commercially available food additives that thicken liquids will increase the viscosity of a sip and may improve swallowing function and reduce a risk for aspiration.
-
A reduction of size of sips and bites, pureeing solid foods and avoidance of simultaneous swallowing of foods with different texture and viscosity, such as solids and liquids, can improve swallowing. Feeding with a particular implement, such as a cup, straw, or spoon, may also improve swallowing.
-
Excessive production of viscous saliva, which often pools in their mouth of OPMD patients, can be relieved by sucking on hard candy, preferably sugarless, can stimulate swallowing and provide temporary relief from drooling. An effective treatment, available by prescription, is atropine eye drops taken on or under the tongue.
-
Expiratory Muscle Strength Training improves effectiveness of the cough reflex and reduces aspiration. Simple accessories can be used for respiratory muscles training, such as inflating balloons, a Tri–Flo device or more professional aids.
For patients who are unable to tolerate oral nutrition despite these measures or who are at high risk for aspiration – enteral nutrition is indicated.
The treatment of muscle weakness that close to the center of the body – is affected by the severity of the injury, which usually worsens over time:
In a situation where the difficulty in operating the muscles close to the center of the body (Proximal Muscles) is mild to moderate – the expression will be difficulty in walking and the solution surprisingly will be walking and fitness, studies show that there is importance and possibility to strengthen the remaining muscle mass by performing fitness and custom exercises. (with a physiotherapist guides) depending on the patient’s ability to “compensate” for the loss of the relative part by weakening the
“injured” part of the muscle.
In a situation where the difficulty in operating the muscles is great and the severity of the injury is severe – we will have to use orthopedic devices such as canes, shoulder pads, walking stick or wheelchair.